Conceptually, accounts receivable reflects a company’s total outstanding (or unpaid) customer invoices. Accounts Receivable (A/R) is defined as payments owed to a company by its customers for products and/or services already delivered to them – i.e. an “IOU” from customers who paid on credit. In this journal entry, both total assets on the balance sheet and total revenues on the income statement increase by $200 on July 10. When the company receives cash for the credit sale on a later date, they will debit cash as it comes in and credit accounts receivable to settle the amount received in cash.
What is the Journal Entry for Accounts Receivable?
Often, a business offers this credit to frequent or special customers who receive periodic invoices. This allows customers to avoid having to make payments as each transaction occurs. Other business routinely offers all their clients the ability to pay after receiving the service. An electricity company is an example of a company with accounts receivable. They provide electricity to a space and wait for payment from their customers. Since issuing an invoice does not involve any change in cash, there is no record of accounts receivable in the accounting records.
Accounts Receivable Turnover (in Times)
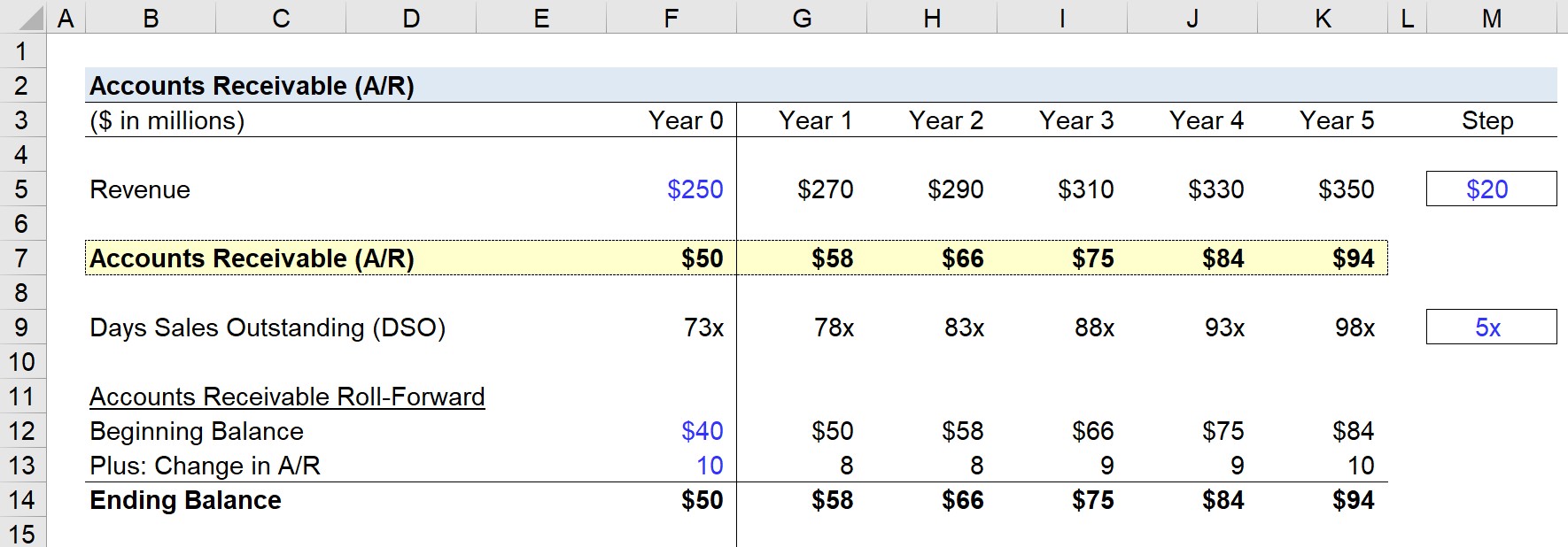
Allowance for doubtful accounts is a contra account on receivables balance and shown in the balance sheet as a negative current asset. Day Sales Outstanding, or DSO, measures the time it takes your Accounts Receivable team to collect an invoice payment. It’s a valuable indicator for assessing the efficiency of your collections process and the credibility of your customers. Having a clear process for managing overdue payment collections ensures that you have the proper documentation if you need to seek formal collections support. Average accounts receivable is the beginning balance + ending balance divided by two. Accounts receivable is the money that customers owe a business for goods or services that have been delivered but not yet paid for.
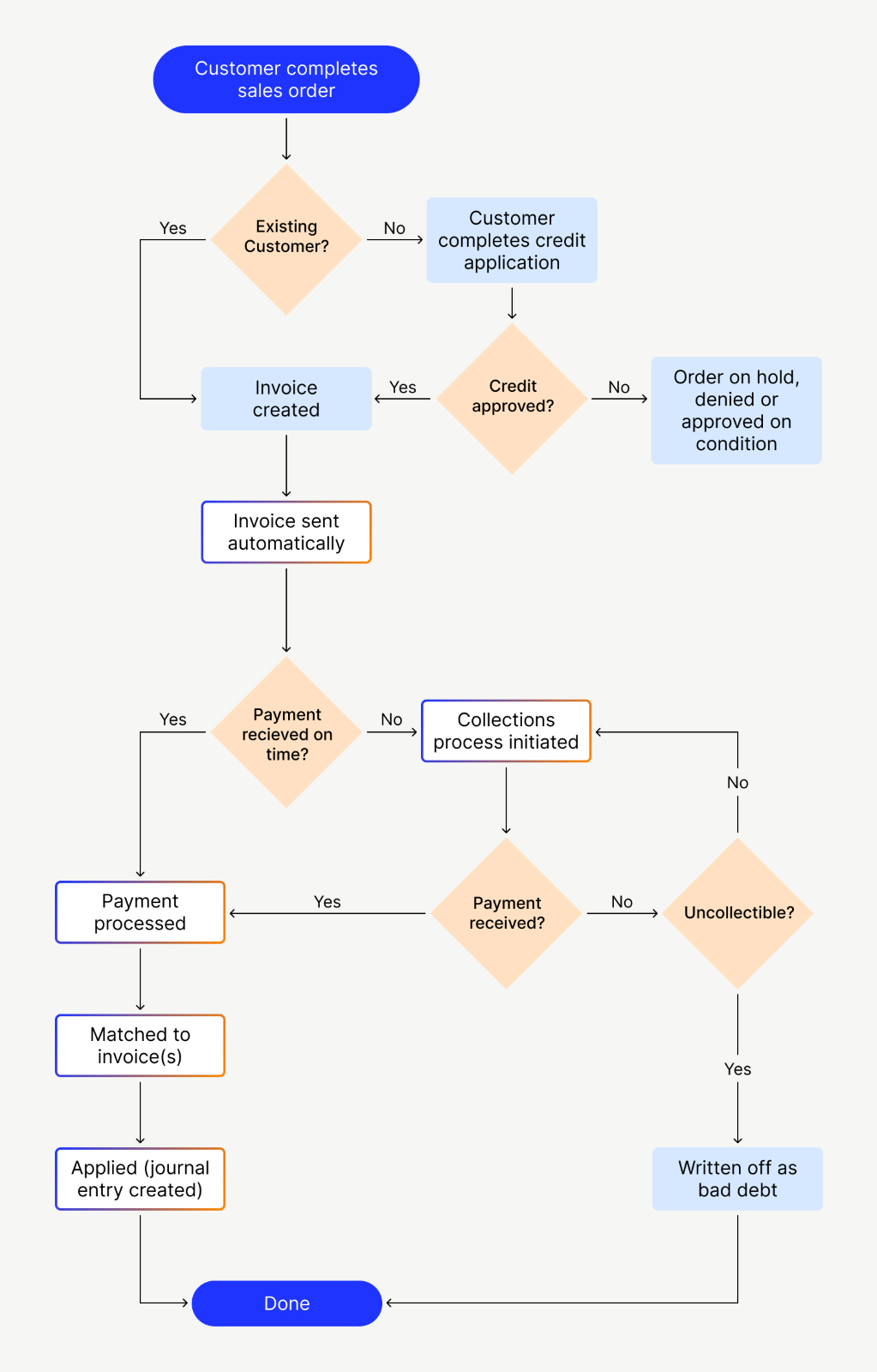
Accounts Receivable Process: Your Step-by-step Guide
Late payments from customers are one of the top reasons why companies get into cash flow or liquidity problems. Here we’ll go over how accounts receivable works, how it’s different from accounts payable, and how properly managing your accounts receivable can get you paid faster. Because they represent funds owed to the company (and that are likely to be received), they are booked as an asset. A receivable is created any time money is owed to a business for services rendered or products provided that have not yet been paid for.
- A/R Aging Report shows all the receivables classified by the day overdue which details all customers that still owe the company.
- A low DSO means that customers are paying promptly after receiving their invoices and that your team is quickly processing the payments.
- To track how well your dunning efforts are going, you should regularly create accounts receivable aging reports.
The term refers to accounts a business has the right receive because of goods and services delivered. If you find that customers are regularly late with their payments, you may choose to extend the length of time before you write off unpaid invoices as bad debt. Keeping track of exactly who’s behind on which payments can get tricky if you have many different customers.
Managing bad debt
On the other hand, the receivable account represents amounts your business is owed. The primary sources of receivables are transactions with customers in which they are allowed to pay later. The forecasted accounts receivable balance is equal to the days sales outstanding (DSO) assumption divided by 365 days, multiplied by 365 days.
Your business may choose to accept some or all of these payment methods as outlined in your sales order and invoice. Accounts Receivable (AR) is the money that customers owe to a business for goods or services states with no income tax provided. When customers make a purchase on credit, that debt is added to the business’s Accounts Receivable. When recording accounts receivable, you want to post the revenue in the month you earn it.
Thus, Ace Paper Mill will collect its average accounts receivables close to 5.66 times over the year ending December 31, 2023. It can also be the case that Lewis Publishers does not make the payment within 45 days. In such a case, Ace Paper Mill would either reach out to Lewis Publishers for payment or hire a collection agency to collect the accounts receivable.
CEI is an important metric for demonstrating that a business can maintain a seamless cash flow process. It also indicates that your customer credit assessment is effective since you have a high ratio of paid invoices to total invoices. It sets in motion the payment process and outlines payment terms, encouraging customers to promptly pay their debts. Ensuring you send invoices promptly sets a strong foundation for the rest of the Accounts Receivable system to proceed. To begin the ordering and Accounts Receivable process, a customer will place an order that needs to be approved by the business.
If takes a receivable longer than a year for the account to be converted into cash, it is recorded as a long-term asset or a notes receivable on the balance sheet. Under the accrual basis of accounting, the account is offset by an allowance for doubtful accounts, since there a possibility that some receivables will never be collected. This allowance is estimate of the total amount of bad debts related to the receivable asset. If a company sells on credit, customers will occasionally be unable to pay, in which case the seller should charge the account receivable to expense as a bad debt.
